The Sino-US Trade War in 2025
The United States and China are economic powerhouses that are constantly caught in an ongoing trade battle with one another. From the onset of the trade war starting in 2018 to the signing of a trade deal in 2020, the trade tensions between these two nations still impact the role of international trade today.
While the initial 90-day Sino-US Tariff Truce has been extended and temporarily de-escalated the tariff war, global uncertainty remains. All eyes are now on November 10, the negotiation deadline that could redefine global trade.
Stay ahead of global trade through the TecEx Tariff Tracker. Track the latest negotiations, tariffs, and policy shifts. Stay informed.
.webp)
Sino-US Trade War | A Brief History
To fully grasp the full extent of today’s Sino-US trade war, we must understand that this rivalry did not happen overnight but is rooted in a complex history shaped by shifting global powers.
In 2020, the trade conflict between the US and China reached a pivotal moment when the Sino-US Phase One trade deal was signed. The purpose was to achieve a bilateral trade rdsbalance between the two countries. China agreed to increase its purchases of American products and services by more than USD 200 billion over two years, and the US decided to lower tariffs on Chinese goods.
However, China fell short of its commitments, leading to unresolved conflict. This conflict quietly lingered until recently, when trade tensions began to flare up again. The renewed friction stems from the new United States Administration’s push for tariff increases, driven by factors such as national security concerns and an imbalance of trade.
Tracking The Sino-US Tit-for-Tat Tariffs in 2025
To better understand the Sino-US trade rebuttal, it is helpful to track the tit-for-tat tariffs imposed between the countries thus far. Here is a short timeline:
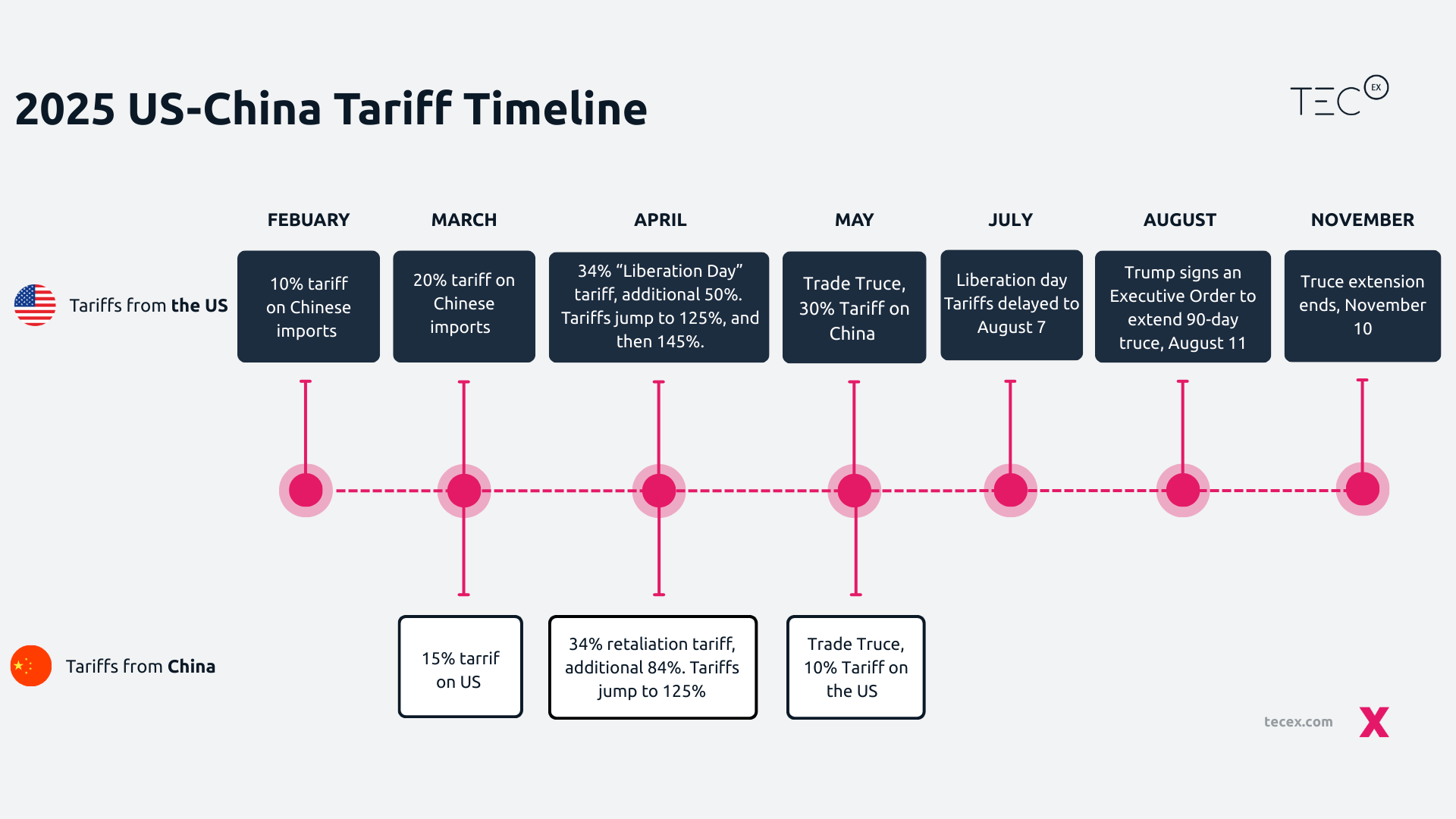
Tariffs between the U.S. and China began rising rapidly earlier this year, peaking at 145%. This steep escalation prompted both sides to agree to a 90-day US-China Tariff Truce on May 10. The US lowered tariffs to 30% for China, while US imports to China face 10%.
Negotiations have been ongoing since the initial US-China Tariff Truce, with tensions rising towards the end of May, just days after the deal.
Both countries have accused one another of violating the truce. The United States limited the opportunities for Chinese students to study in the US and tightened export controls on AI software. At the same time, China responded with delays on critical shipments such as rare earth materials vital for electronics.
Negotiations on what is to come are still ongoing. We wait to see what will be agreed upon after the truce, setting the stage for renewed economic and geopolitical tension.
Key Terms and Goals for The Truce
Why Have a Truce?
To fully understand the US-China Tariff Truce, we must ask: what made it necessary in the first place?
In economic terms, the trade deficit was the key driver behind U.S. President Donald Trump’s aggressive tariff approach. The US relies more heavily on China for goods, particularly in technology and electronics, where it imports 440 billion USD and exports 145 billion USD. The US government, therefore, wants to reduce the United States’ dependence on China by strengthening the US economy and increasing the purchase of American-made products. This is where the China-US trade war has taken center stage.
As a result, the world has seen a change in logistics and supply chains with increased transshipments while watching the ongoing rebuttal and daily tracking of tariffs.
What This Means For Importers
The pause has also given businesses a moment to breathe and reassess their future of logistics and operations.
Many businesses experienced temporary relief, helping ease the financial strain caused by aggressive tariffs. This has given them a chance to regroup and plan ahead in an unpredictable trade environment.
Beyond the corporate impact, the pause has opened up a diplomatic window, allowing the US and China more time for negotiations. This brief period of calm is crucial to de-escalating trade tensions, re-evaluating the current situation, and potentially reshaping global trade.
US-Sino Trade War Impact on Tech Supply Chains and Key Industries
This US-China tariff war created chaos across sectors. Many companies with manufacturers in China halted shipments, leading to shipping delays. Tech companies have also been hit. Apple’s stock prices dropped by 3% following the announcement of the tariffs. Firms in the semiconductor industry also have to rethink their logistics to avoid high price hikes, with talks of adding a surcharge to their products.
In May alone, Chinese exports to the US declined by 34.5%, resulting in a significant loss. This sharp decline underscored the need for a trade truce to allow businesses to plan and give relief while the future of tariffs awaits.
However, since the implementation of the US-China Tariff Truce, shipments have surged back with unprecedented momentum. It is becoming a race against time to get goods from Asia into the US before the end of the Truce. Reflecting the urgency, Chinese port congestion has seen its busiest weeks on record, with a 6% jump in traffic as congestion intensifies.
%20(1).webp)
Future Outlook and Strategic Considerations for Sino-US Uncertainty
As tensions are temporarily eased, countries are now faced with more uncertainties about the US-China trade outlook for the future. We cannot predict the outlook of global trade, but being aware of tariffs is the first step in navigating supply chains.
There was a glimmer of progress from the two days of negotiations in London in June, during which US and Chinese officials met behind closed doors to nail down a potential framework. Shortly after, Trump announced on Truth Social that “our deal with China is done.”
July talks in Sweden seemed productive, but President Trump’s decision to extend the truce came nearly two weeks after they occured. This decision will maintain the current trade ties and facilitate continued negotiations, but the verdict on November 10 could go either way. It all comes down to whether China satisfactorily addresses America’s economic and national security concerns, and whether China sees any new agreement with the US as mutually beneficial.
However, with no formal approval in place, uncertainties remain. The Executive Order extending the truce stipulated no changes other than a new deadline for the ongoing negotiations. We can, therefore, only watch and wait for what the future of trade between the US and China holds.
While we wait for clarity, make sure to work with an Importer of Record to help with multi-scenario planning, supply chain diversification, and compliance optimization.



