Harmonized System (HS) codes provide a universal language for the trade of products across borders. It allows customs officials, traders, and governments to be able to categorize and identify a product, thereby allowing for smooth customs clearance, adherence to international trade regulations, and promoting efficient supply chains. In the vast realm of global trade, enabling efficient communication is paramount to ensuring a seamless experience in customs. HS codes provide exactly that. From avoiding stuck shipments to ensuring accurate duty calculation, let’s dig into the basics of HS codes.
Understanding HS Codes
Similar to the purpose of incoterms, Harmonized System (HS) codes are a universal language for the classification of products. HS codes enable customs officials to identify the product and apply the appropriate import duty (and any additional taxes or trade measures based on that good). Each HS code corresponds to a specific tariff rate, which varies depending on the type of product, country of origin, and so on.
Developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO), HS codes are a six-digit nomenclature system that identifies products based on nature, composition, and intended use. Some countries add to this harmonized system while retaining the general rule of interpretation. For example, the U.S. International Trade Commission developed a Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS code) for US import clarification.
Worried your products are being incorrectly classified? Don’t disrupt your supply chain.
What Are HS Codes Used For?
The use list for HS codes is endless.
Ranging from internal taxes and tariffs, trade policies, monitoring of controlled goods (like dual-use tech goods!), rules of origin, transport statistics, economic research and analysis – HS codes are used across the board.
According to the WCO, over 98% of the commodities within international trade are classified according to the harmonized system.
HS codes cover thousands of commodity groups – from aerospace parts to tech being shipped to a data center. All is done in an effort to ensure that no matter what country of import, the system can be used to apply the appropriate customs tariff structure.
The WCO regularly updates HS codes to accommodate technological advancements, health and safety concerns, environmental challenges, anti-terrorism, and border security.
HS codes play an important role in determining the origin of goods. For example, preferential tariffs under Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and Most Favored Nation (MFN) tariffs are set based on HS code classifications. Correct identification of the HS code is key to ensuring the appropriate rule of origin is applied to the product under an FTA.
How are HS Codes Used by Customs Officials?
HS codes streamline clearance processes by aiding customs authorities in quickly identifying products, applying appropriate tariffs, and gathering internal trade statistics. Using HS code stats you are able to assess a country’s major exports. For example, between the years of 2020-21, Japan’s fastest export markers for integrated circuits were China and Vietnam. Furthermore, by ensuring goods are correctly identified, this lessens the risk of misinterpretation. This is of particular importance when trading dual-use goods. As such, HS codes are an important tool for all institutions involved in global trade.
HS codes, under the guidance of the WCO, facilitate several crucial aspects of international trade.
The Importance of HS Codes
- Uniform Classification: HS codes allow for clear communication between customs authorities of different countries, serving as a universal language for categorizing goods and reducing soft inefficiencies.
- Efficient Customs Processing: Prior to import, HS codes make it easier for the correct documents to be sourced. With these standardized codes, customs officials can quickly and accurately identify goods, assess duties, and process imports and exports.
- Customs Duty Payment and Other Taxes: Using the HS code, you can easily calculate the customs duty payable for the goods imported, thereby allowing for efficient budgeting, projection, and financial planning.
- Global Trade Statistics: HS codes are instrumental in gathering and analyzing trade data, which is vital for economic planning and policy-making.
- Regulation: The stats are also used for the regulation of internal taxes, trade policies, monitoring of controlled goods (like dual-use gear!), rules of origin, international organizations, and the private sector.
Common HS Codes Challenges and Solutions
The complexities surrounding HS codes are due to the sheer volume and diversity of products, making the system large and complex.
- Accurate Classification: One of the biggest challenges in using HS codes is ensuring the right code is used. This is made further complex by including additional digits, such as HTS codes, making it difficult to keep track of code variations. The vast range of products and their specific classifications under the HS system can lead to confusion. To mitigate this, businesses should invest time in understanding the HS nomenclature and seek advice from customs experts when necessary. TecEx’s compliance database ensures that each and every HS code is accurate and can be applied to all our client’s shipments ensuring seamless customs clearance.
- Keeping Up to Date: The HS codes are subject to periodic updates to reflect changes in technology, industry, and trade patterns. Businesses need to stay informed about these changes. For example, in the 2022 HS code revision, smartphones received their own tariff provision. This revision not only impacts the actual device but also its corresponding accessories and component parts.
- Management of HS Codes: Manually managing large amounts of HS code data that is subject to change can be risky. Not only can this lead to potential stuck shipments, but also any unforeseen changes in duty tariffs can impact your bottom line.
- Meeting Specific Country Requirements: Different countries may interpret HS codes in slightly varying ways. It’s essential to understand these nuances, especially when trading with multiple countries. This is where a customs specialist can guide you through the complexities and manage the entire process.
HS codes contribute to reducing trade barriers and enhancing global cooperation.
What Happens If You Use The Wrong HS Codes?
Using the incorrect HS code is one of the major reasons for stuck shipments. If the incorrect code is used, the shipment will be delayed for inspection. Moreover, the importer will likely have to pay additional fees/penalties.
Using the wrong HS code can have the following implications:
- Non-compliance penalties: Monetary penalties that can run into the millions.
- Risk of delays and storage charges: As the goods will need to be inspected, the shipment will not be cleared until the discrepancies have been thoroughly investigated. This could lead to the goods requiring storage until the issues are resolved.
- Seizure of goods: The shipment may be seized indefinitely until customs officials correctly classify the goods.
- Regulatory risk: Incorrectly classifying your goods can attract regulatory agencies to intervene and lead to the importer paying higher duties or a fine for inaccuracy.
The responsibility of ensuring the use of the correct HS code is down to the importer or exporter. When importing in your own entity’s name, this means that all of this risk and responsibility lands on you.
HS Codes and TecEx
No one expects you to become an expert in HS codes and customs compliance. If done incorrectly, even the smallest mistake can lead to damaging repercussions and stuck shipments. Reach out to TecEx today, and let us handle customs compliance for you.
Through years of experience, we have built a database of HS codes for tech products, making customs compliance a breeze. TecEx helps ease the risks and responsibilities associated with importing high-value tech equipment. We classify your goods, provide upfront costings, and move your shipment through customs seamlessly.
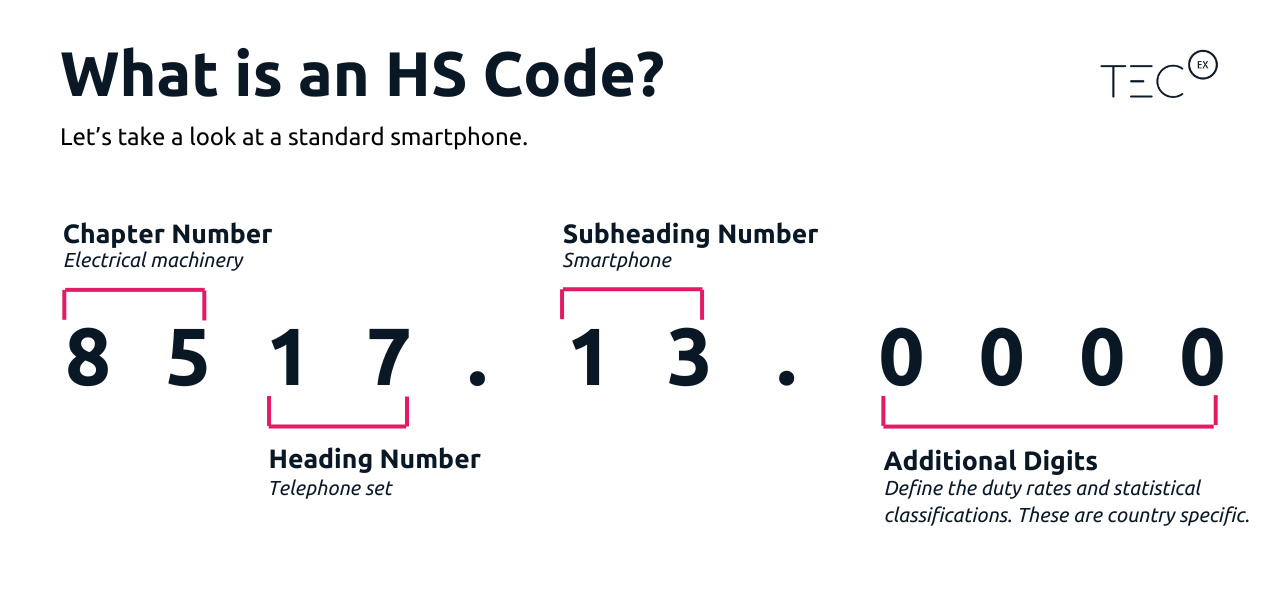
The breakdown of the meaning behind the HS code:
Code Type
HS Codes
Digits
1-2
Meaning
The chapter in the HS Nomenclature that the goods are classified in. There are 99 chapters grouped into topics.
Code Type
HS Codes
Digits
3-4
Meaning
The heading in the chapter your item falls under.
Code Type
HS Codes
Digits
5-6
Meaning
The subheading that contains your item’s code.
Code Type
HS Codes
Digits
6+
Meaning
This consists of a ‘rate line’, which helps CBP work out the duty you’ll pay, and the ‘statistical suffix’ or ‘category’, which is used for trade data collection.
HS Code FAQs
Are HS codes required to ship products internationally?
In short, it depends on the country. While not universally mandated, they are crucial in facilitating international trade.
Are HS codes different for each country?
HS codes are a universal tool for product classification. However, some governments add additional digits to the HS number to further categorize products into certain categories. This is seen with HTS codes.
Are HS codes mandatory?
This is country dependant. Certain countries, such as many within the European Union, mandate HS codes for all imported goods, while some countries only require HS codes for shipments of a certain value threshold. An IOR can help your business navigate this and provide HS codes for your products.
Let’s find a solution that
works for you
Fill in the form to get in touch, and our expert team will contact you with a bespoke customs compliance solution to suit your needs.
Let’s find a solution that works for you
Fill in the form to get in touch, and our expert team will contact you with a bespoke customs compliance solution to suit your needs.