In the fast-paced and interconnected world of international trade, proper management of goods and technologies is essential to ensure customs compliance, efficient supply chain operations, and adherence to international trade regulations. Export Control Classification Numbers (ECCN codes) play a pivotal role in achieving these objectives. Let's delve deeper into ECCN codes, their significance, and how they contribute to the world of shipping and global trade compliance.
Quick Brief of ECCN Codes
ECCNs are vital codes assigned to items listed on the Commerce Control List (CCL), playing a pivotal role in export control classification. These codes help in categorizing items based on their technical specifications, capabilities, and potential applications. By assigning an ECCN, exporters can determine the necessary export licenses and any restrictions associated with the specific items.
ECCNs are instrumental in maintaining national security by ensuring the accurate classification of goods.
For example, an item primarily designed for civilian purposes might also possess features that could be utilized for military applications. Export control regulations are in place to prevent such items from reaching destinations where they could be repurposed for military use, thus safeguarding against potential threats.
What are Export Control Classification Numbers (ECCN) Codes?
Export Control Classification Number (ECCN) codes are five-character alphanumeric codes used on the Commerce Control List (CCL) to categorize and control the export of dual-use goods and technologies. These codes are part of the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), which are housed by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
While they come from the United States, ECCN codes are used by many countries to regulate international trade. Each ECCN code corresponds to a specific commodity or technology – such as servers, chips and cables – to help determine whether an item is subject to export controls and which licensing requirements apply. Take a laptop, for example, if the encryption uses a key length exceeding 256 bits and the laptop is being exported to a country on the BIS Entity List (entities denied certain export privileges), a license under the EAR might be required.
What are ECCN Codes used for?
ECCNs are used by the United States Department of Commerce to identify and control the export of dual-use items. These items have both civilian and military applications, and the ECCN code helps to determine whether an export license is required and what restrictions may apply.
Why Do I Need an ECCN Code for Global Trade Compliance?
For companies operating in the global rollout of technology, ECCN codes are a fundamental aspect of their overall trade compliance strategy. Keeping up to date with the latest ECCN updates and trade regulations is crucial to maintaining a compliant and efficient international trade operation. It enables businesses to adapt swiftly to regulatory changes and make informed decisions while managing risks associated with global trade.
ECCN codes are essential in customs compliance. Customs authorities across the world use these codes to assess shipments, verify their legitimacy, and enforce trade regulations. By correctly identifying the ECCN code of goods being exported, companies can determine the applicable trade restrictions. This enables businesses to adhere to trade regulations, ensuring a smooth customs clearance process and minimizing the risk of penalties for non-compliance.
ECCNs can help indicate whether certain products have been banned from the destination country or reveal blacklisted traders. Since these goods have military implications, incorrectly classifying goods can have severe repercussions.
Understanding ECCNs and Their Relationship to Banned Products
ECCNs serve as indicators of the level of control required for exporting specific items, but they don’t explicitly denote banned products. However, they can offer valuable insights into potential restrictions.
Here’s how ECCNs relate to banned products in different regions:
- United States: The US Department of State administers trade sanctions against certain countries. For example, limitations on exporting encryption technology may apply to countries listed on the State Department’s List of EAA Sanctions Destinations such as Russia, Belarus, and Iraq.
- China: China maintains its own export control regulations. ECCNs associated with dual-use goods may trigger scrutiny from Chinese customs if they conflict with China’s rules on technology exports.
- European Union (EU): The EU has its own export control framework, which may vary from that of the US. ECCNs assigned to civilian aircraft could prompt additional examination if they possess the potential for military conversion under EU regulations.
While ECCNs offer guidance, it’s crucial to remember that they’re just one aspect of export compliance. Exporters should thoroughly review the regulations of the destination country to ensure adherence, irrespective of ECCN classifications.
Want to find out more? Schedule some time with a TecEx global trade expert
What Happens if I Have the Wrong ECCN Number?
The wrong product classification may result in a mistaken determination of which agency has jurisdiction over the goods you wish to export, the inability to properly determine if an export license is required, misuse of license exceptions, and more.
Getting the ECCN wrong in the export process can spell big problems for your business and cross-border expansion.
Some of the major consequences of having the wrong ECCN code include:
Ways to Avoid These ECCN Challenges
Overall though, there are three ways to help you avoid these misclassifications:

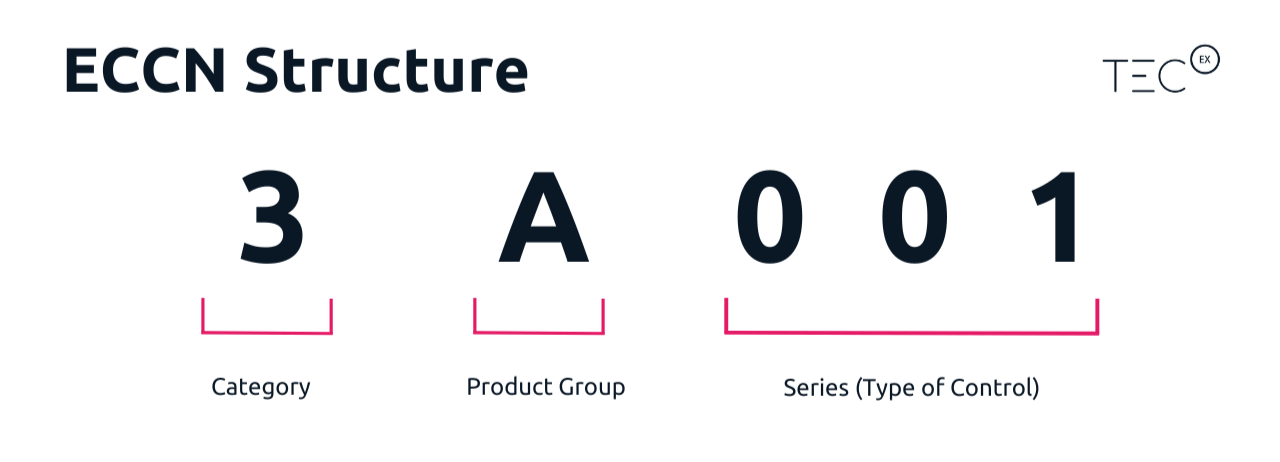
The Structure of Export Control Classification Number
The first digit identifies the broad category of the item listed on the CCL (e.g., 0 for nuclear materials, 1 for materials, chemicals, microorganisms, and toxins, 2 for materials processing, etc.).
The second digit identifies the product group within the category (e.g., A for equipment, assemblies, and components, B for materials, C for components, D for software, etc.).
The third digit is used for further subcategorization.
The fourth and fifth digits are used for specific control reasons or for items that do not fit neatly into other categories.
The Categories and Product Groups of ECCN Codes
All ECCNs are listed in the Commerce Control List (CCL), which is divided into ten broad categories, and each category is further subdivided into five product groups. The first character of the ECCN identifies the broader category to which it belongs, and the second character identifies the product group.
How to Find an ECCN Code?
There are four ways to determine your product’s Export Control Classification Number (ECCN).
Consult an Export Compliance Expert
Enlisting the services from the likes of an Exporter of Record (EOR) ensures that the export of goods out of the country meets all compliance requirements and legal regulations. TecEx’s EOR services include everything from categorizing your tech products and classifying the required ECCN to sourcing the required export compliance documents and taking on the related risks and responsibilities of your export so you don’t have to.
Go to the Source
Contact the manufacturer, producer, or developer of the item you are exporting to see if they have classified their product and can provide you with the ECCN. If they have exported the item in the past, it is likely they have the ECCN.
Self-Classify
In order to perform a self-classification, you must have a technical understanding of your item, and you need to be familiar with the structure and format of the CCL.
Request an Official Classification From the Bureau of Industry and Security
Submit a commodity classification request online through the Simplified Network Application Process – Redesign (SNAP-R). You must obtain a Company Identification Number (CIN) before accessing the online SNAP-R system and submitting your request.
Do All Products have an Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)?
No. Many commercial goods are not on the CCL and do not have an ECCN. These goods are designated as EAR99.
Furthermore, material that is inherently military, related to nuclear technology or protected infrastructure information, as well as some satellites, are in a jurisdiction other than the EAR, such as the ITAR, and may be under stricter controls.
ECCN Codes and TecEx
ECCN codes are key tools in the world of shipping, customs compliance, and global trade. By properly classifying goods and technologies, businesses can navigate the complexities of international trade regulations, ensure efficient supply chain management, and safeguard against legal repercussions.
With TecEx, you can confidently pursue international trade while remaining compliant, efficient, and competitive in the global economy. Our compliance database and in-country experts ensure that your goods will be accurately identified so the appropriate trade compliance documentation is sourced and collated.
Now You Know: ECCN Codes Go Beyond Physical Goods.
With the ever-expanding digital landscape, intangible items like software and technology exports have become prevalent, and they, too, may require an ECCN code for export control purposes. Classifying intangible items accurately is equally critical, as the mismanagement of software and technology exports can have far-reaching consequences on your global trade compliance.
ECCN Codes FAQs
How do ECCN numbers differ from Schedule B codes?
ECCN focuses on security control and export licensing.
Schedule B code focuses on trade statistics and product categorization.
It’s crucial to use the correct code for your specific needs. ECCNs are essential for determining export control requirements, while Schedule B codes are necessary for accurate reporting of export data. If you’re unsure which code applies to your situation, consult relevant government resources or seek guidance from an export professional.
Are ECCN codes and HS codes the same?
Harmonized system codes or HS codes and ECCNs are similar but are considered independent. Both HS codes and ECCNs describe the nature of the product and classify them accordingly. That is where that similarity begins and ends.
While ECCNs dictate what licensing is required, HS codes determine the duties and taxes associated with that product.
Numerous factors influence the ECCN number and licensing requirements of a particular product. This means one HS code may have several ECCNs and vice versa.
Who uses ECCN codes?
ECCN numbers are primarily used by two groups of people:
- Exporters:
Individuals and businesses: Anyone looking to export goods, software, or technology from the United States to another country will need to determine the ECCN for their item. This helps them understand if an export license is required and what regulations apply.
Freight forwarders and customs brokers: These professionals assist with international shipments and rely on ECCNs to ensure compliance with export regulations.
- Government agencies:
U.S. Department of Commerce Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS): This agency manages the Commerce Control List (CCL) where ECCNs are listed, and maintains the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) that govern them.
Other government agencies involved in export control: Depending on the item being exported, agencies like the State Department or Department of Defense might also utilize ECCN information.
Let’s find a solution that
works for you
Fill in the form to get in touch, and our expert team will contact you with a bespoke customs compliance solution to suit your needs.
Let’s find a solution that works for you
Fill in the form to get in touch, and our expert team will contact you with a bespoke customs compliance solution to suit your needs.


